ncp for normal newborn baby
 Nursing Care Plan For Newborn Baby - Newborn baby
Nursing Care Plan For Newborn Baby - Newborn baby4 postpartum thrombophlebitis Surface Nursing Care Plans is commonly frequent during the period that during and is seen more in women who experience varicose veins. Postpartum (DVT) and surface thrombophlebitis have been attributed to pelvic vein trauma by the pressure exerted by the present fetal part, the deteriorated circulation caused by mechanical edema and the coagulation changes related to the high amount of estrogen produced during pregnancy. The thrombosis that involves only the superficial veins of the leg or thigh is unlikely to result in pulmonary emboli (PE). Although approximately 50% of customers with DVT are asymptomatic, DVT is more severe in terms of possible complications, such as post-trombotic syndrome, chronic venous insufficiency and destruction of venous valves. Nursing Care PlansThe care plan objectives for a customer with postpartum thrombophlebitis include improving, facilitating thrombo resolution, promoting optimal comfort, preventing complications and providing information and emotional support. Here are four (4) (NCP) and for postpartum thrombophlebitis: Perfusion of altered peripheral tissue may be related to Possibly demonstrated by desired results Nursing Interventions Rationale Capillary monitor recharge time; Assess the positive sign of Homans (alf on dorsiflexion foot). DVT can prolong hair recharge time. The positive sign of Homans is not a reliable indicator of DVT. Evaluate the circulation, asymmetry, sensory and motor function of the extremity; Observe edema from the groin to the feet; Measure and record calf/thigh circumference from both legs as appropriate. Proximal progression report of inflammation, travel pain. Symptoms help differentiate between superficial thrombophlebitis and DVT. The localized edema, redness, warmth and tenderness are indicative of superficial involvement. The filling and coldness of the extremity are more DVT features. The participation of the DVT calf vein is usually associated with the absence of edema; mild to moderate edema suggests the participation of the femoral vein, and severe edema is characteristic of thrombosis of the ileofemoral vein. Evaluate breathing and hide for lung sounds, notice cracks or rub friction. Investigate reports or feelings of . Pulmonary congestion, sudden acute chest pain, anxiety, shortness of breath, rapid heart rate and hemoptisi are characteristic of pulmonary embolism, especially in the DVT. Instruct the client to avoid massage or rub the affected limb. Massaging the limb increases the risk of loosening the thrombo that can become ambuli. Keep rest in bed with elevation of lower feet and legs at the heart level during the acute phase. It reduces the possibility of loosening thrombos and creating ambuli. It quickly empties the superficial and warm veins and keeps the veins collapsed, thus increasing the venous return. Raise the client's legs when you rest or sit in a chair. It reduces inflammation of the tissues and quickly emptys the superficial and warm veins, preventing over-distension and thus increasing the venous return. Instruct the customer to avoid crossing the legs or wearing constrictive clothing. It promotes the movement restriction that damages the flow, thus increasing the venous stasis, pain and trauma. Encourage a greater intake of 2500 ml/day liquid unless counterindivided It reduces the viscosity of the blood and minimizes the possibility of thrombo formation. Emphasize the importance of deep breathing exercises. Increase negative pressure on the chest that helps to empty large veins. Facilitate and assist with active or passive ROM while at rest; Help with the gradual resumption of the ambulation as recommended. Increases venous performance, decreases venous stasis and maintains strength. Apply hot, wet or heating pads to the affected extremity as ordered. It promotes circulation, reduces inflammation and improves venous performance. Apply elastic support hose. Precaution is advised to prevent a turning point. Useful during the acute phase of surface thrombosis, as they exert a steady and evenly distributed pressure on the entire surface of the calves and thighs, decreasing the caliber of the surface veins, improving blood flow to the deep veins and reducing stasis Apply mechanical devices such as sequential compression media, thromboembolic media (TED) as indicated. It reduces venous stasis in the lower extremities and increases the flow of blood to the veins of the large legs that are for the formation of thrombos. Laboratory study monitor: The increase in levels may indicate a thrombi formation. It measures the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy. Hemoconcentration and increases the viscosity of blood and venous stasis, which promotes the formation of thrombos. Manage as indicated: The reproductive tract can result in septic pelvic thrombophlebitis. It can be used for treating acute or massive DVT to prevent walver damage and development of chronic venous insufficiency. Heparin usually starts several hours after the end of thrombolytic therapy. Heparin is usually preferred initially, due to its rapid and predictable antagonistic action towards thrombin formation and the prevention of further formation of clots. Due to its large molecular size, heparin does not go as coumarin derivatives do; however, coumarin, which blocks the formation of vitamin K protrombine, can be used for long-term therapy after discharge. Prepare for surgical intervention as indicated. Thrombectomy (thrombo excision) is usually done if the inflammation extends proximally or the circulation is severely compromised. Recurrent thrombotic episodes that do not respond or contraindicate to anticoagulant therapy may require the insertion of a lower filter (IVC). Acute Diagnosis of Pain It may be related to Possibly demonstrated by desired results Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluate the degree and characteristic of discomfort or pain using scale 0-10; palp the leg with caution. Watch the surveillance of the limb. The degree of pain is directly related to the extent of the arterial intervention, the degree of hypoxia and the degree of edema associated with the development of the thrombo in the swollen vein wall. The customer can protect or immobilize the affected limb to decrease the painful sensations associated with muscle movement. Changes in the characteristics of pain may indicate progression of the problem/development of complications Monitor vital signs, notice high temperature or pulse. Lifting vital signs may indicate increased pain, or occur in inflammatory response and process. The fever can contribute to general discomfort. Note reports of sudden or acute chest pain, dyspnea, tachycardia or apprehension. These signs and symptoms indicate a complication of DVT. Encourage the change of position, keeping the extremity elevated. Promotes venous performance; decreases and muscle spasms. Raise the affected extremity; provide cradle standing. Encourages venous return, facilitates circulation. The standing cradle maintains the pressure of the mantels outside the affected leg, thus reducing the discomfort of pressure Keep the bed during the acute phase. It reduces discomfort associated with muscle contraction and movement. Minimizes the possibility to loosen thrombo. Explain procedures, treatments and interventions of nursing. The client's involvement in nursing care increases their sense of control and decreases their level of anxiety. Apply wet heat to the extremity. It causes vasodilation, which increases circulation, relaxes muscles and can stimulate the release of endorphins. Manage medicines as indicated: Reduces fever and inflammation. It relieves pain and decreases muscle tension, promoting /rest Deficient knowledge Diagnosis may be related to Possibly demonstrated by desired results Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluate customer knowledge and understanding of the disease process. Correct as necessary. It helps to identify specific needs and clarify previous information. Provide information on management and diagnostic tests. Identify signs and symptoms that require notification from the healthcare provider; for example, pain, swelling, and sensitivity in one of the legs. It can increase understanding and decrease anxiety associated with home condition and management. The evolution of conditions and/or the development of treatments requires rapid evaluation and possible changes in therapy to prevent serious complications. Demonstrate the use of antiembolic media. Encourage the elimination of elastic media for short intervals at least twice a day. Continuous constriction can alter or reduce superficial perfusion, leading to muscle fatigue. The elimination of elastic media allows the detection of increased vascular involvement or inflammation. Explain the purpose of the bed or activity restrictions needs for a proper rest. Rest reduces the oxygen and nutrient needs of the tissues involved and decreases the risk of thrombosis fragmentation. Balancing rest with activity prevents depletion and deterioration of cellular perfusion. Educate about safety measures to prevent bleeding, such as the use of an electric shaver to shave, the use of soft toothbrush, avoiding walking barefoot. The alterations in the clotting process can lead to a greater tendency to bleed, which may indicate the need to alter anticoagulant therapy. Draw purpose, of anticoagulant. Emphasize the importance of taking the medication as prescribed. It promotes customer safety by reducing the risk of inadequate therapeutic response/deterrent side effects. Identify possible interactions between other oral medications (e.g., , , , and vitamins). Estrés needs to read labels of free selling medication ingredients (OTC). Oral anticoagulant therapy may last 3-4 mo and anticoagulant therapy and may cause problems or require drug dose alterations if it is allowed to interact with other medications. and excess alcohol decreases protrombin activity; vitamin K in multivitamin increases protrombin activity; antibiotics alter intestinal flora and may interfere with vitamin K synthesis; barbiturates increase the metabolism of coumarinic drugs. Identify anticoagulant effects that require medical attention, for example, mucous membrane bleeding, continuous cutting/puncture rezuzation, severe bruising after minimal trauma, petechiae development Early detection of harmful effects of therapy (time prolongation) allows timely interventions and can prevent serious complications. Stress the importance of medical follow-up/ laboratory test. The understanding that the close supervision of the anticoagulant/therapy is necessary (the range of therapeutic doses is narrow and complications can be fatal) promotes the participation/adherence of the client to the therapeutic regime. Diagnostic Anxiety of washing It may be related to Possibly demonstrated by desired results Nursing Interventions Rationale Explain the disease, diagnostic procedures and treatment regimen. Promotes the learning and participation of the customer in care; decreases the unknown. Supervising vital signs and behavioral signs as restless, irritability and crying. It can reveal a change in the level of anxiety and reflects a decrease in the ability to cope with events. Involve clients and family members in the development of a care plan; review instructions and restrictions. It allows them to have a sense of control over the situation; it provides information and allows the client and other significant ones to understand the purpose of interventions and restrictions. Help the customer take care of himself and the baby. Customer anxiety can minimize when meeting needs and is able to adjust and commit and perform child care tasks. Encourage the use of relaxation techniques. Offer an opportunity to verbalize concerns. Relaxation prevents muscle fatigue and allows the customer to rest; the expression of concerns reduces emotional tension, diminishing anxiety. Encourage frequent contact, in person or by phone, with the spouse and children if the client is hospitalized. Encourage the regular "escope" with the condition that allows. It helps reduce feelings of separation and isolation. It facilitates the transition to home. Determine the early availability and effectiveness of support after download. Prioritize responsibilities/domestic tasks. Helps identify specific needs, encourages troubleshooting to meet customer/family needs before the customer is downloaded. See social services, visiting, home care agency, as appropriate. You may need additional support to facilitate family recovery/recovery needs. See You may also like the following positions and care plans: Maternal and Neonatal Care PlansChild Care Programs related to the care of the pregnant mother and her baby. See maternity care plans and obstetric nursing: LEAVE A REPLY Save my name, email and website in this browser for the next time you comment. NURSING ESSENTIALS is a nursing education and lifestyle website aimed at helping registered nurses and nurses with knowledge for progression and empowerment of their nursing careers. Since we started in 2010, Nurseslabs has become one of the most reliable nursing sites helping thousands of nurses to achieve their goals. Our ultimate goal is to help address the shortage of nursing by inspiring aspiring nurses that a career in nursing is an excellent choice, leading students to become RNs, and for the working nurse – helping them succeed in their careers! 2021 Nurseslabs ← Ut at Omnibus Glorificetur Deus! Privacy Policy

NCP-Newborn | Breastfeeding | Breast Milk

Nursing Care Plan For Newborn Baby - newborn baby
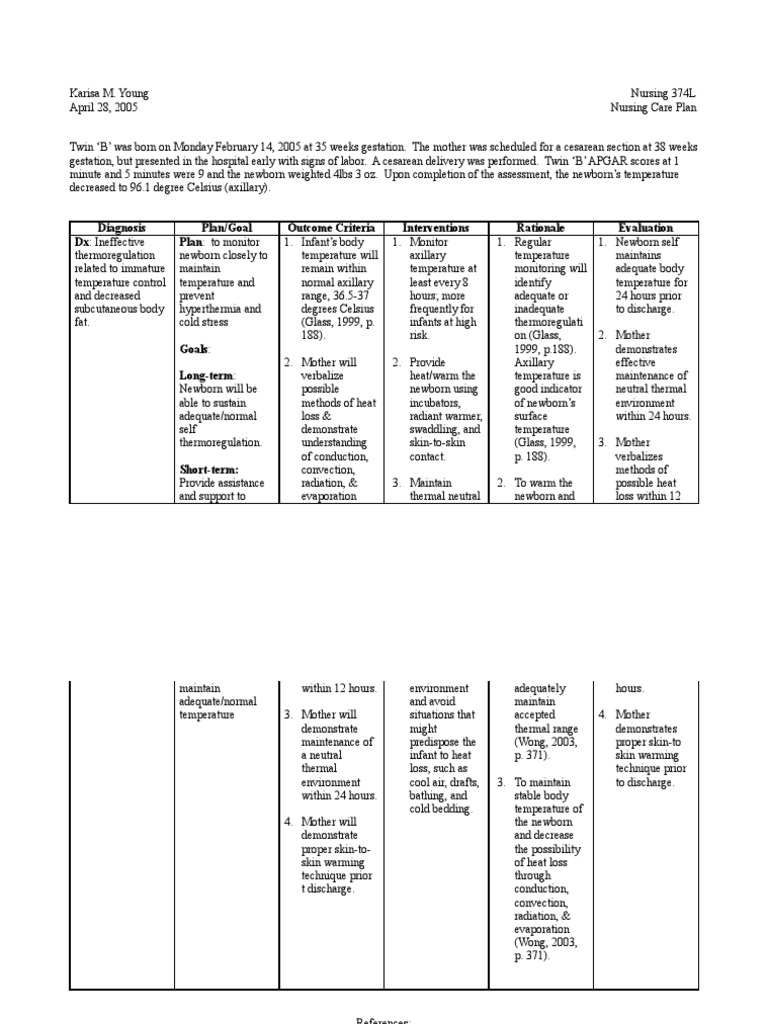
Care Plan For Newborn Baby - Newborn baby
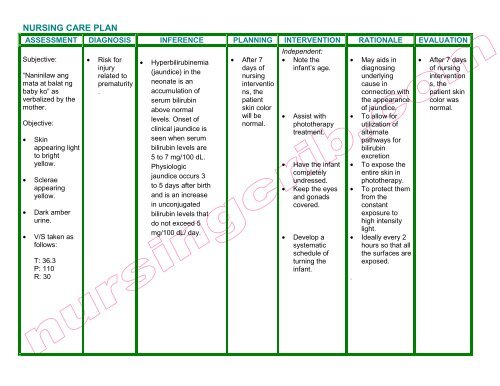
ncp jaundice.pdf - Nursing Crib

Care Plan Infant | Hypothermia | Nursing

Ncp Hypothermia

Pin on Nursing

NCP-NEWBORN.doc - NURSING NURSING CARE CARE PLAN PLAN ASSESSMENT Objectives acrocyanosis Capillary refill time of 3 seconds Apnea cool pale extremities | Course Hero

NCP NEWBORN | Thermoregulation | Heat Transfer

NCP-NEWBORN.doc - NURSING NURSING CARE CARE PLAN PLAN ASSESSMENT Objectives acrocyanosis Capillary refill time of 3 seconds Apnea cool pale extremities | Course Hero

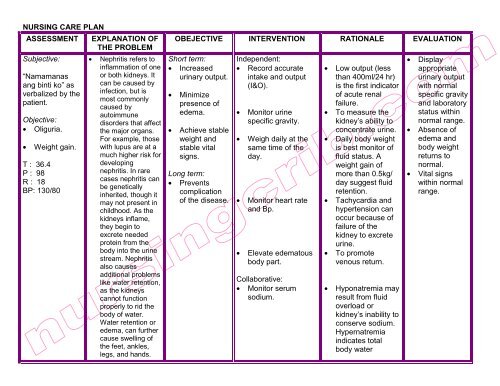
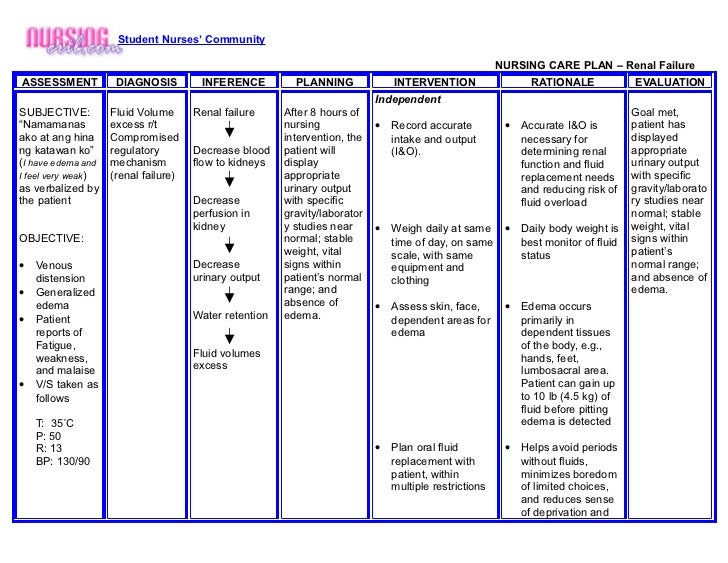
newborn nursing care plan with refernces | Breastfeeding | Infection
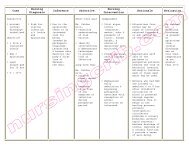
DUTY NCP-OBward.pdf - Nursing Crib
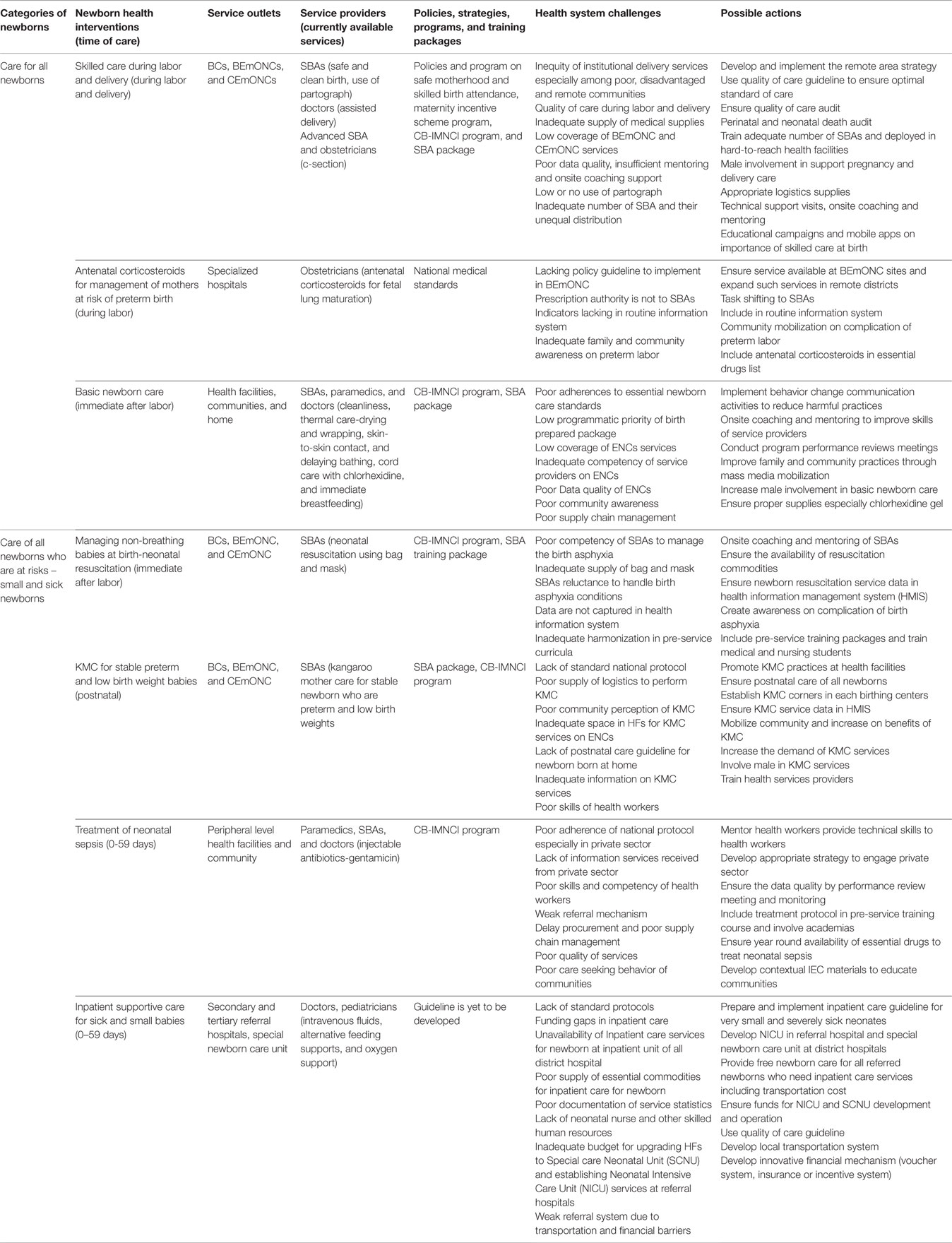
Frontiers | Newborn Health Interventions and Challenges for Implementation in Nepal | Public Health

NCP-Sleep Deprivation | Sleep | Wellness

Ncp On Premature Baby Development - Newborn baby
NCP-NEWBORN.doc - NURSING NURSING CARE CARE PLAN PLAN ASSESSMENT Objectives acrocyanosis Capillary refill time of 3 seconds Apnea cool pale extremities | Course Hero

Early‐Life Gut Microbiome—The Importance of Maternal and Infant Factors in Its Establishment - Kapourchali - 2020 - Nutrition in Clinical Practice - Wiley Online Library
Factors associated with newborn care knowledge and practices in the upper Himalayas

Fluid volume deficit | Breastfeeding | Infants
Nursing Care Plan For Meconium Aspiration Syndrome

13 NCP ideas | nursing care plan, nursing care, nursing diagnosis
Cuidados integrales de enfermería en un lactante con encefalopatía isquémica hipóxica relacionada con la asfixia perinatal
normal lab values chart nursing pdf - Objektiv

92124988 case-study

PDF) Enteral Nutrition Support of the Preterm Infant in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
![3987978 Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Thermoregulation [vylygz5ejelm] 3987978 Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Thermoregulation [vylygz5ejelm]](https://idoc.pub/img/crop/300x300/pd49pkk758n9.jpg)
3987978 Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Thermoregulation [vylygz5ejelm]

NCP for RDS | Medical Specialties | Clinical Medicine
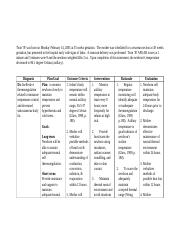
Nursing Care Plan NCP Nursing Crib - induced.info

PDF) Oral Pathology in Paediatric Patients

Postpartum Careplan.docx - Nursing of the Childbearing Family Nursing Care Plan(ADPIE Assessment Objective Data General Information Patient Initial JM | Course Hero

Neonatal hypothermia

NCP Risk for Injury | Preterm Birth | Childbirth

NCP-NEWBORN.doc - NURSING NURSING CARE CARE PLAN PLAN ASSESSMENT Objectives acrocyanosis Capillary refill time of 3 seconds Apnea cool pale extremities | Course Hero

13 NCP ideas | nursing care plan, nursing care, nursing diagnosis

36 Labor Stages, Induced and Augmented Labor Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs
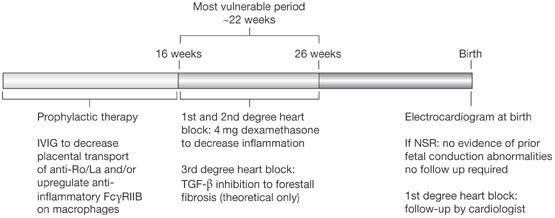
Cardiac manifestations of neonatal lupus erythematosus: guidelines to management, integrating clues from the bench and bedside | Nature Reviews Rheumatology
Specialty Practice
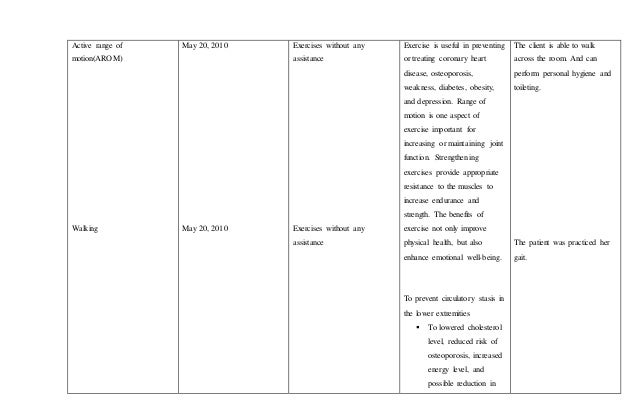
92124988 case-study
Cuidados integrales de enfermería en un lactante con encefalopatía isquémica hipóxica relacionada con la asfixia perinatal

Nursing Care Plans | Nurse Key
Posting Komentar untuk "ncp for normal newborn baby"